What is Programming?
Programming is a way of telling computers to do a task in a particular manner.But the computer only understands 0's and 1's, so that's why various language comes into the picture, It's the kind of language that is readable by humans and also can write or tell the computer to do some task in the readable language, not in 0's and 1's, so after that, there is compiler who converts all the readable code to machine code or 0's and 1's so the computer can understand the instructions given to it.
Types Of Languages
1:) Procedural Languages
In Procedural languages there are well-defined steps to perform the task, or we can say that there is a procedure like first this thing will execute then this and then this, there is a step-by-step instruction to compose a program, Contains systematic order of statements of functions and commands to complete a task. For example=> C, java, Fortran etc.
2:) Functional Languages
In Functional languages, we write pure functions to perform the task, Used in situations where we have to perform lots of different operations with the same set of data, It is like for every problem we have to write a function to solve the problems, It is not like procedural language to follow the steps, we just have to write functions to perform the task. For example => javascript, python, etc,
3:) Object Oriented Language
In Object Oriented Language it revolves around the object, what an object is like Code + data. Like suppose we have to create a program, so in object-oriented we define the object of that and use that data anywhere in the program with the help of the object we have created, the object is like a real entity or we can say value or an instance of the class. what is instance it is kind of a part we can say.
Don't worry we will discuss the class instance object in the OOPs blog I will tell you every detail in the OOPS blog till now just remember the object is an entity in the forms of code + data.
For example, =>Like Humans are a class and we human beings are the object of that class or instance of the class. Java follows procedure and Object Oriented Approach.
Static and Dynamic Languages
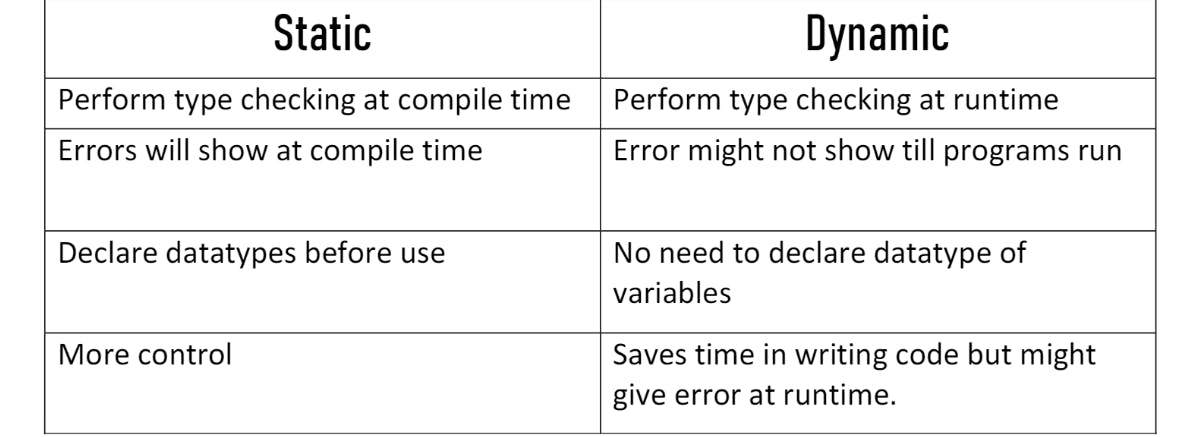
In this above Image Static type checking at compile time means when all the source code is converted to machine code it is compiled time checking and In Dynamic Languages type checking is done at the run time. For example => In static Languages, if we declare a = 7; it will give an error while the program is compiled and in dynamic Languages a = 7 will not show an error till the programs run. What exactly the Compile time is like when the program is converted into machine code during the conversion time the programming languages should know what is the type of the a in Static Type Languages. and the type checking in runtime is known as Dynamic Languages.
Memory Management
There are two types of Memory in Programming Languages
Stack Memory
Heap Memory
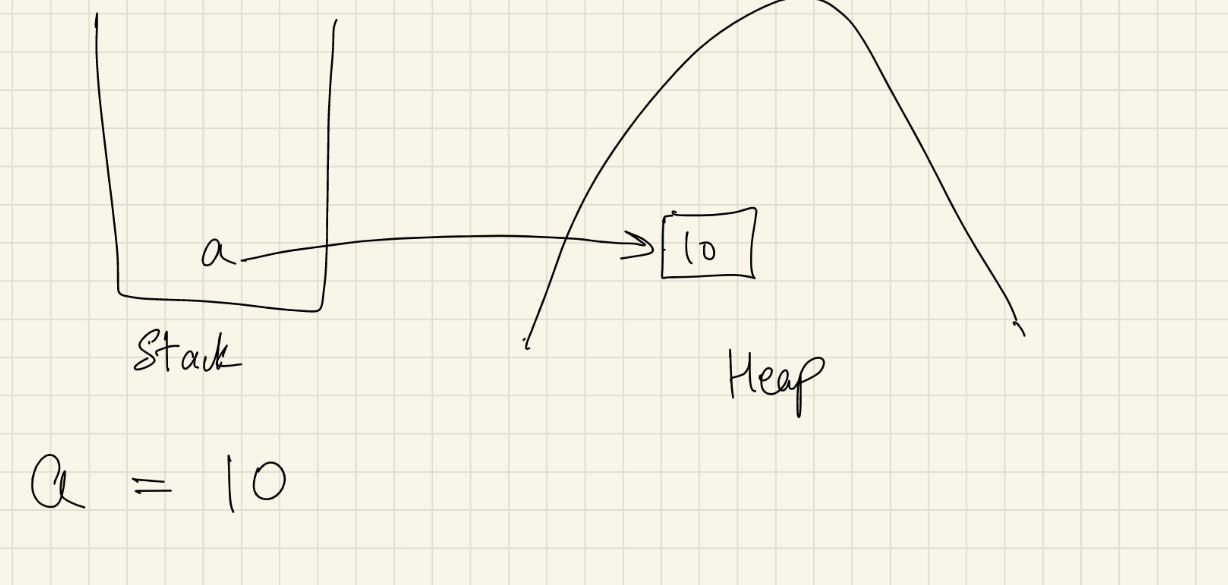
Stack Memory stores the reference variable pointing to the object in the Heap Memory.
And Heap Memory Store the Actual value of the Object
For example=> int a= 10; so, a is a reference variable stored in the stack memory pointing towards the heap memory for the actual value.
In java there is no pass-by-value, pass-by-reference, it is a pass-by-reference value.
Points to remember
More than one reference variable points to the same object.
If anyone changes the object value it will be reflected in all other objects.
If there are no reference variable points to the object, the object will destroy by the garbage collector.
If you liked my content, do kindly like and share in your network. And don't forget to subscribe to the newsletter to NEVER miss an article.

